Color Blindness
Color blindness, also known as color vision deficiency, is a condition that affects an individual’s ability to perceive or differentiate certain colors. While most people can perceive a wide range of colors, individuals with color blindness have difficulty distinguishing specific colors or may see them differently. This article aims to shed light on the causes, types, and available treatments for color blindness.
Causes of Color Blindness:
Color blindness is primarily caused by abnormalities or deficiencies in the photopigments within the cones of the retina, specialized cells responsible for color vision. The most common cause of color blindness is an inherited genetic mutation on the X chromosome, making it more prevalent in males. This condition is known as congenital color blindness. Acquired color blindness can occur later in life due to certain diseases, medications, or eye injuries that affect the normal functioning of the cones.
Types of Color Blindness:
Color blindness is categorized into three main types, depending on which colors are affected:
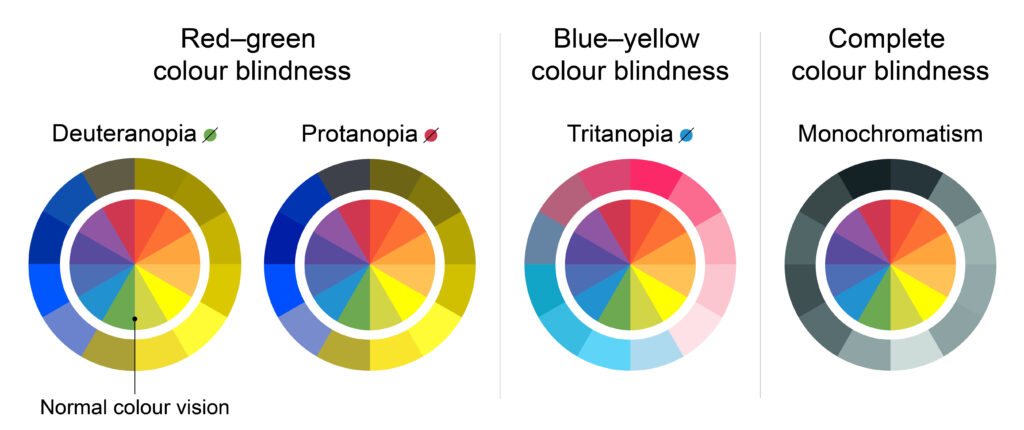
1. Red-green color blindness: This is the most common type and refers to the difficulty in distinguishing between red and green hues. It can range from mild to severe, with individuals experiencing varying levels of impairment in perceiving these colors.
2. Blue-yellow color blindness: Individuals with this type have trouble differentiating between shades of blue and green, as well as between yellow and violet. Blue and yellow hues may appear similar or indistinguishable.
3. Total color blindness: Also known as achromatopsia, this rare form of color blindness renders individuals unable to perceive any color at all. Their vision is limited to shades of gray.
Treatment of Color Blindness:
While there is no known cure for congenital color blindness, certain measures can help individuals cope with the condition:
1. Color filters and corrective lenses: Specialized lenses and glasses with color filters can enhance color perception and improve the ability to differentiate between certain colors. These aids work by selectively filtering light wavelengths, enhancing color contrast.
2. Vision therapy: Some individuals with color blindness can benefit from vision therapy, which involves exercises and training to help improve color discrimination skills. However, the effectiveness of this approach may vary among individuals.
3. Assistive technology: In the digital age, there are various smartphone apps, computer software, and color-assistive devices available that can help individuals with color blindness identify and distinguish colors. These tools use color-correcting algorithms or provide color information through alternative means, such as text or patterns.
4. Education and adaptation: Learning to recognize patterns, rely on color cues in the environment, and use context clues can help individuals with color blindness navigate daily life more effectively. Awareness of their color vision deficiency and understanding their limitations can enable them to make informed choices and seek appropriate assistance when needed.
Conclusion:
Color blindness is a visual impairment that affects how individuals perceive and distinguish colors. While it may pose certain challenges in daily life, various strategies and technologies exist to assist individuals with color blindness. Although there is no definitive cure, understanding the causes and types of color blindness can promote awareness, acceptance, and support for those affected by this condition. By embracing advancements in assistive technology and making practical adaptations, individuals with color blindness can lead fulfilling lives, appreciating the vibrant world around them in their own unique way.


Leave a Reply